
The algorithms that calculate the isoelectric point of proteins and peptides use the Henderson Hasselbalch equation.
Calculate pi isoelectric point full#
Enter a single protein (raw sequence): Full Length: 0. Use Protein Isoelectric Point when you want to know approximately where on a 2-D gel a particular protein will be found. It tells us when a particular molecule has attained the electrically neutral state, and the pI can affect the solubility of said molecule. Protein Isoelectric Point calculates the theoretical pI (isoelectric point) for the protein sequence you enter.

that give the boundaries to its existence. The isoelectric point is an essential topic in chemistry and biochemistry. The pI is given by the average of the pKas that involve the zwitterion, i.e. The balanced charges may acquire positive or negative charges in a particular. As long as you have any two of the three values to input, the calculator will work fine for you. The isoelectric point (PI) calculates the pH where charges are balanced. Remember, our tool works in reverse and any other order you want to. Input these values in the calculator and the result is 6.55 6.55 6.55 Say you have molecule X, its p K a = 3.7 pKa = 3.7 p K a = 3.7 and p K b = 9.4 pKb = 9.4 p K b = 9.4. This value indicates the pH at which your molecule carries no net electric charge. The result is that molecule's isoelectric point (pI value).Can you explain this answer Related Test.
Calculate pi isoelectric point how to#
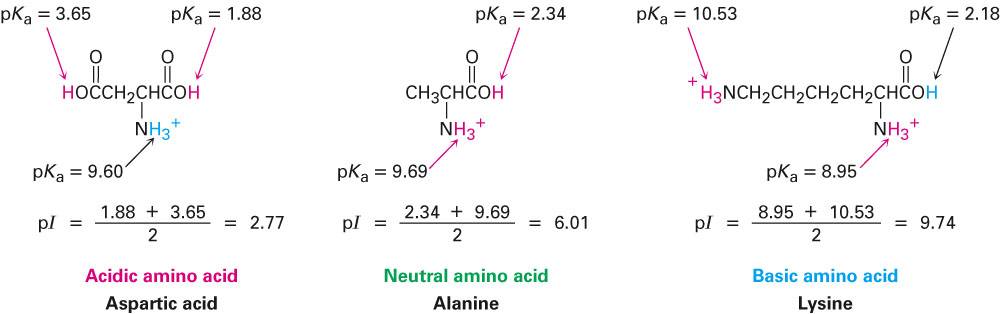
Now, coming back to the point at hand, how to use the isoelectric point calculator? Follow the given steps, and that's it: Chemistry Question > Calculate the isoelectric point (pI) of lysin.

The dissociation constant represents the capability of a substance to dissociate into ions in a solution. What are pKa and pKb values, you might wonder? These are the dissociation constants of acids and bases. It determines the isoelectric point of molecules based on their pKa and pKb values. By lysine the side chain $-(CH_2)_4\mboxOH$ is an even weaker acid $$ so the IEP is 5.66Īnd every amino acid has more or less contribution to the IEP of a protein.Our isoelectric point calculator is a tool you would love to use on the go.By glycine the side chain $-H$ is neutral (while the amino and carbonic acid groups are not) so the IEP is 5.97.This isoelectric point depends on the side chains: Every amino acid has a different isoelectric point: a pH where they do not carry electric charge. The isoelectric point (pI) of a molecule is the pH at which the molecule carries no net charge.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
